Blood Pressure Machines: Monitoring Your Health The Guide
Introduction:
Maintaining good health is a priority for individuals of all
ages. Regular monitoring of vital health parameters, such as blood pressure, is
a fundamental aspect of healthcare. With the advent of technology, blood
pressure machines have become essential tools for at-home health management. In
this detailed and lengthy blog, we'll delve deep into the world of blood
pressure machines, exploring their importance, types, how to use them
correctly, and the significance of tracking blood pressure for overall
well-being.
Understanding the Importance of Blood Pressure
The Vital Sign:
Blood pressure, often referred to as the "silent
killer," is a vital sign that indicates the force of blood against the
walls of your arteries. Maintaining a healthy blood pressure level is crucial
for overall well-being.
Health Implications:
High blood pressure, or hypertension, is a leading risk
factor for heart disease, stroke, and other health conditions. Monitoring blood
pressure helps in early detection and management, reducing the risk of
complications.
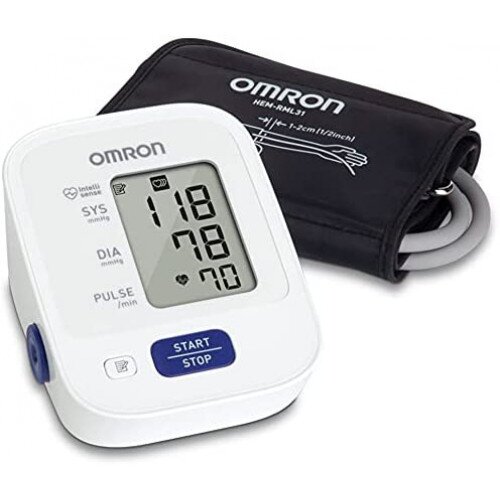
Types of Blood Pressure Machines
Manual Blood Pressure Monitors:
Sphygmomanometers: These are the classic blood pressure
monitors with an inflatable cuff, a pressure gauge, and a stethoscope. They
require manual inflation and listening for Korotkoff sounds to determine blood
pressure.
Automatic Blood Pressure Monitors:
Digital Automatic Monitors: These are easy to use and provide
a digital reading. They inflate and deflate the cuff automatically, making them
convenient for self-monitoring.
Wrist Monitors: Wrist blood pressure monitors are compact and
portable. They are worn on the wrist, making them suitable for on-the-go
monitoring. However, they may be less accurate than upper arm monitors.
Finger Monitors: These are the smallest and most portable
options but are less accurate and not recommended for routine monitoring.
Ambulatory Blood Pressure Monitors:
Holter Monitors: These are wearable devices that continuously
monitor blood pressure over a 24-hour period. They are often used in clinical
settings for detailed assessments.
How to Use a Blood Pressure Machine Correctly
Preparation:
Sit in a quiet, comfortable place: Find a quiet, relaxed
environment fo r measurements.
Rest before measuring: Sit quietly for at least 5 minutes
before taking your blood pressure.
Measurement:
Position the cuff: Place the cuff around your upper arm at
heart level.
Follow device instructions: Start the measurement according
to the manufacturer's guidelines.
Record your measurements: Note the systolic and diastolic
readings.
Interpretation:
Normal: Blood pressure readings of 120/80 mm Hg or lower are
considered normal.
Elevated: Readings between 120/80 mm Hg and 129/89 mm Hg
indicate elevated blood pressure.
Hypertension Stage 1: Readings between 130/90 mm Hg and
139/89 mm Hg are considered stage 1 hypertension.
Hypertension Stage 2: Readings of 140/90 mm Hg or higher
indicate stage 2 hypertension.
Seek medical advice: Consult a healthcare professional if you
consistently have high readings.
Tracking Blood Pressure for Well-Being
Regular Monitoring:
Consistent monitoring of blood pressure is essential for
understanding your health status. Tracking helps in identifying trends and
deviations, enabling timely interventions.
Lifestyle Modifications:
Tracking your blood pressure readings can motivate you to
m ake positive lifestyle changes. This may include dietary adjustments, exercise
routines, and stress management.
Medication Management:
For individuals with hypertension, tracking blood pressure is
crucial for managing medication effectiveness. It aids in determining whether prescribed
medications are controlling blood pressure adequately.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, blood pressure machines are valuable tools for
monitoring one of the most critical aspects of your health. With different
types of monitors available, you can choose the one that suits your needs and
preferences. By understanding the correct usage and significance of tracking
blood pressure, you can take proactive steps towards maintaining optimal health
and well-being.









